Batteries are devices that store and release electrical energy. The thermal management of a battery is the process of regulating the temperature of the battery to ensure optimal performance and prevent damage. There are several methods of thermal management, including passive and active cooling.

Passive cooling relies on the natural convection of air to cool the battery, while active cooling uses mechanical means, such as fans or water circulation, to remove heat from the battery.
Batteries are a critical component of many electronic devices and need to be properly managed to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Thermal management is one way to keep batteries functioning properly by regulating their temperature. There are several ways to manage battery temperature, but the most common is through active cooling, which uses a fan or other means to circulate air around the battery.
Other methods include passive cooling, which relies on materials that absorb and dissipate heat, and phase change materials, which change from solid to liquid at a certain temperature to help regulate heat. The type of thermal management used will depend on the device and its intended use. For example, laptops and smartphones typically use active cooling because they generate more heat than other devices.
However, some devices like electric vehicles may use all three methods depending on how much power they use and how demanding their environment is. Thermal management is important for keeping batteries working properly because it helps prevent them from overheating or becoming too cold. Overheating can damage the battery cells and shorten their lifespan while being too cold can make them less effective at storing energy.
By keeping the battery at an ideal temperature, you can help extend its life and ensure it performs as intended. You can check this article, 3 Cell Battery How Long Does It Last?
Thermal Management of Electric Vehicle Battery Systems
As the number of electric vehicles (EVs) on the road continues to rise, so does the need for effective thermal management systems for their battery packs. Battery thermal management is critical to ensuring the safety and performance of EVs, as well as maximizing the lifespan of the batteries. There are a number of different approaches to thermal management for EV battery packs, including active cooling and passive cooling.
Active cooling systems use fans or other mechanical means to circulate coolant around the battery pack, while passive cooling relies on convection and radiation to dissipate heat. The most important factor in choosing a thermal management system for an EV battery pack is its ability to maintain the optimal operating temperature range for the batteries. This range varies depending on the type of battery chemistry used but is typically between 20-30°C.
Another important consideration is the weight and space requirements of the thermal management system. For example, an active cooling system will generally be heavier and take up more space than a passive system. Thermal management systems can have a significant impact on both the performance and longevity of EV batteries.
When selecting a system for your vehicle, it is important to consider all factors involved in order to make an informed decision that best meets your needs.
Battery Thermal Management Review
As battery electric vehicles (BEVs) become more prevalent, the need for efficient thermal management of batteries becomes increasingly important. Thermal management is a key factor in determining the range and performance of BEVs, as well as the lifetime of the battery pack. In this blog post, we will review some common methods for the thermal management of batteries, including active cooling and passive cooling.
| Active cooling systems | Active cooling systems use external sources of energy to cool the battery pack, while passive cooling systems rely on heat transfer to ambient air or water. Common active cooling methods include forced air cooling and liquid cooling. |
| Passive methods | Passive methods include natural convection and radiation cooling. Forced air-cooled systems are typically used in smaller BEVs with lower power demands, such as passenger cars. The battery pack is enclosed in a housing with one or more fans that circulate air around the cells to dissipate heat. Liquid-cooled systems are typically used in larger BEVs with higher power demands, such as buses or trucks. |
The battery pack is enclosed in a housing with a coolant fluid circulated around the cells to remove heat. Natural convection and radiation cooling system do not require an external energy source but may be less effective than active or passive methods depending on the environment and application. Thermal management is essential for the safe operation and the long life of BEV battery packs.
Appropriate selection of thermal management method depends on many factors including vehicle size and power requirements, operating environment, climate conditions, etc. Trade-offs between weight, volume, complexity/reliability/maintainability must be considered when designing a thermal management system for a BEV application.
Thermal Management of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles
Thermal management of lithium-ion batteries is critical to the performance and safety of electric vehicles. The battery pack must be kept within a certain temperature range to operate properly and to avoid thermal runaway, which can lead to fires or explosions. There are several ways to manage the battery pack temperature.
Active cooling using air or liquid coolants is one option. Another is to use passive cooling techniques such as thermal insulation and phase change materials. The choice of the cooling system will depend on the design of the vehicle and the operating conditions.
For example, a vehicle that will be driven in hot climates will require a more robust cooling system than one that will be driven in cooler weather. Whatever cooling system is used, it must be designed to maintain the battery pack within its safe operating temperature range.
Battery Thermal Management System
Thermal management of batteries is critical to their safe and reliable operation. Overheating can lead to degradation and failure of the battery, as well as pose a safety hazard. An effective thermal management system will keep the battery within its operating temperature range, even during extreme conditions.
There are two main types of thermal management systems for batteries: active and passive. Active systems use external energy sources, such as fans or pumps, to circulate coolant around the battery. Passive systems rely on natural convection and radiation to dissipate heat from the battery.
Both types of systems have their advantages and disadvantages. Active systems are more effective at cooling the battery but require more maintenance than passive systems. Passive systems are simpler and require less maintenance but may not be able to adequately cool the battery during extremely hot conditions.
The choice of thermal management system depends on many factors, including the type of battery, operating environment, and desired level of reliability. For example, lead-acid batteries typically use passive cooling due to their low power density, while lithium-ion batteries often use active cooling because of their high power density.
Battery Thermal Management Course
Whether you’re a new battery thermal management engineer or an experienced one, this course is designed to give you a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and best practices in designing efficient and reliable battery thermal management systems. You’ll learn about the different types of heat sources in batteries, how to model them, and what design trade-offs must be considered when selecting thermal management components and strategies. The course will also cover important topics such as system integration, control algorithms, manufacturing considerations, and regulatory compliance.
By the end of the course, you’ll have all the tools you need to design efficient battery thermal management systems for a variety of applications.
Thermal Management in Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as technology improves and the cost of ownership decreases. However, one of the challenges with electric vehicles is thermal management, which is the process of regulating the temperature of the vehicle’s battery pack and motor. Thermal management is important in electric vehicles because it can help to increase range and performance, while also prolonging the life of the battery pack which can affect cold temperature.
There are a few different strategies that can be used for thermal management in electric vehicles, including active cooling and passive cooling. Active cooling involves using fans or other mechanical means to move air around the battery pack and motor. This can be an effective way to cool down these components, but it does require additional energy from the battery pack, which can reduce range.
Passive cooling relies on convection and radiation to dissipate heat away from the battery pack and motor. This doesn’t require any additional energy from the battery pack, but it can be less effective than active cooling in some cases. The best thermal management strategy for an electric vehicle will vary depending on a number of factors, including driving conditions, climate, and how much power is being used by the vehicle.
In general, though, it’s important to keep an eye on battery temperature and make sure that it doesn’t get too hot or too cold. If you’re not sure what strategy is best for your electric vehicle, consult with a qualified technician or dealer.
Battery Thermal Management System Matlab
A battery thermal management system (BTMS) is a system that controls the temperature of batteries. BTMSs are used in a variety of applications, including electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and military systems. BTMSs typically use sensors to monitor the temperature of batteries and then use cooling or heating elements to keep the batteries within the desired temperature range.
The specific design of a BTMS will vary depending on the application. For example, an electric vehicle may have a more complex BTMS than a consumer electronic device. There are many benefits to using a BTMS.
By keeping batteries within their optimal temperature range, BTMSs can extend the life of batteries and improve their performance. Additionally, BTMSs can help prevent safety issues associated with overheating batteries. If you are designing a system that uses batteries, it is important to consider whether or not you need a BTMS.
Depending on the application, a BTMS may be essential for safe and reliable operation.
Thermal Management System in Vehicles
Most people are familiar with the engine cooling system in their vehicle, but many don’t know about the other thermal management system components that keep your car running at its best. The thermal management system in vehicles is responsible for managing the temperatures of all the electronic components and systems in your vehicle. Just like our bodies, electronic systems need to be kept within a certain temperature range to function properly.
If they get too hot, they can overheat and fail. That’s why vehicles have a variety of cooling methods to keep everything working correctly, even in extreme conditions. The main component of the thermal management system is the coolant.
Coolant circulates through all the electronic components and systems to absorb heat and then carries it away to be cooled by either air or water. Depending on the vehicle, different coolants may be used including ethylene glycol or propylene glycol-based liquids, air, or water. There are also a variety of cooling methods that can be used depending on the application.
Air-cooled systems use fans to circulate air around heated components while liquid-cooled systems use circulating coolant to transfer heat away from critical components. Water-cooled systems are often found in high-performance applications where space is limited and weight needs to be minimized such as in race cars or aircraft. No matter what type of system or coolant is used, proper maintenance is essential for keeping your vehicle’s thermal management system working correctly.
Regularly check fluid levels and condition, clean debris from radiators and filters, and inspect hoses for leaks or damage. By following these simple steps, you can help ensure that your vehicle’s thermal management system will keep your car running cooler and longer!
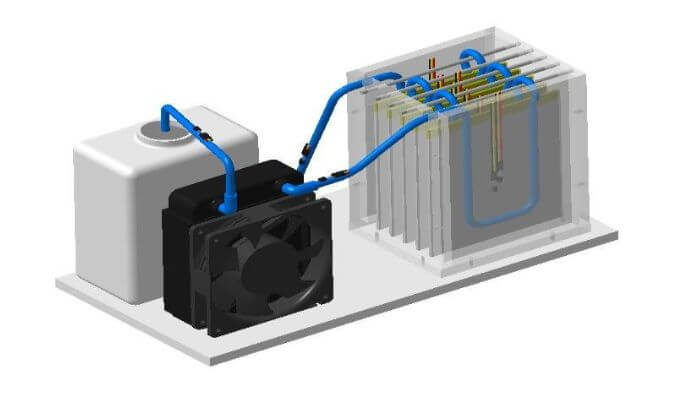
FAQs
Why Thermal Management of Battery is Important?
Batteries are an essential part of many electronic devices, from cell phones to laptops to electric cars. Without batteries, these devices would not be able to function. However, batteries can be hazardous if they are not managed properly.
Thermal management is a critical part of battery safety. When batteries overheat, they can catch fire or explode. This is why it is important to keep batteries cool, especially when they are being charged.
There are several ways to manage battery temperature:
| Use a cooling pad or mat when charging your device | This will help dissipate heat away from the battery. |
| Avoid charging your device in direct sunlight or in a hot environment | The heat will cause the battery to overheat more quickly. |
| If possible, charge your device overnight when the ambient temperature is cooler | This will help prolong the life of your battery and prevent overheating. |
| Keep an eye on the temperature of your device while it is charging | If it starts to feel warm, unplug it immediately and allow it to cool down before continuing use. |
What is the Main Object of Thermal Management of Battery Pack?
The primary objectives of battery pack thermal management are to maintain the cells within their safe operating temperature range and to minimize capacity fade due to high temperatures. There are several different approaches that can be taken to achieve these goals, and the most effective approach will vary depending on the specific application and operating environment. Some common methods of thermal management include forced air cooling, liquid cooling, phase change materials, and active/passive thermal control.
What is Vehicle Thermal Management?
Vehicle thermal management is the process of regulating the temperature of a vehicle’s interior and engine. It is important for both comfort and safety, as well as for optimal engine performance. There are several methods of thermal management, including ventilation, insulation, and cooling systems.
Ventilation is the most basic form of thermal management and involves allowing fresh air to circulate inside the vehicle. This can be accomplished by opening windows or using fans. Insulation helps to keep heat in or out, depending on the needs of the situation.
Cooling systems use either air or fluid to lower the temperature inside the vehicle. Thermal management is an important consideration in any type of vehicle, but it is especially crucial in electric vehicles. This is because electric vehicles have a higher risk of overheating due to their battery packs.
Thermal management systems help to prevent this from happening by keeping the batteries at a safe operating temperature.
What are Thermal Management Solutions?
When it comes to managing the temperatures in electronic devices, there are thermal management solutions available to help. These solutions can be used to regulate the temperature of individual components or an entire system. There are a number of different types of thermal management solutions, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common type of thermal management solution is active cooling. This involves using fans or other forms of forced air to remove heat from the device. Active cooling is typically more expensive than other methods, but it is also more effective at keeping temperatures under control.
Another advantage of active cooling is that it can be used to cool multiple devices at the same time. Passive cooling relies on natural convection and radiation to remove heat from the device. Passive cooling is typically less expensive than active methods, but it is not as effective at regulating temperature.
One advantage of passively cooling systems is that they often require less maintenance than active cooled ones. Thermal management solutions are important for keeping electronic devices functioning properly and within their operating temperature limits. By choosing the right solution for your needs, you can keep your devices running cooler and improve their performance and lifespan.
Conclusion
There are several factors that can affect the temperature of a battery, including charging/discharging cycles, ambient temperature, and exposure to sunlight. Managing these factors can help to prolong the life of a battery and keep it performing at its best.