In the physical sciences, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. This law is a direct consequence of the fact that matter and energy can neither be created nor destroyed; they can only be transformed from one state to another. So if matter and energy cannot be created, then how is it that the universe continues to expand?

The answer lies in understanding what we mean by “universe.” In cosmology, the universe refers to everything that exists—all space, all matter, all forms of energy. It is important to remember that our universe is not closed; it is constantly interacting with other universes beyond our own.
These interactions allow for the exchange of matter and energy between universes, which ultimately leads to the expansion of our own. So while it may seem like an impossible feat, the universe expanding is simply a result of its never-ending interactions with other universes. And as long as there are other universes out there for ours to interact with, it will continue to grow larger and larger.
The universe is expanding because energy is being created. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. So, the universe is constantly creating new energy to fuel its expansion.
This might seem like a contradiction, but it’s actually quite simple. The universe is filled with matter and radiation, which are constantly interacting and converting energy from one form to another. For example, when a star forms, gravitational potential energy is converted into heat and light.
This heat and light then radiate out into space, powering the expansion of the universe. So, if energy cannot be created, how is the universe expanding? By constantly converting existing energy into new forms that can drive expansion.
If Energy Cannot Be Created, How Does It Exist?
In the physical sciences, energy is the property of matter and space that manifests as the ability to perform work. Energy exists in several forms, including kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, electromagnetic radiation, chemical energy, nuclear energy, and rest mass energy.
| The first law | The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. In other words, the total amount of energy in the universe is constant. |
| The second law | The second law of thermodynamics says that when energy is transformed from one form to another there are always some losses (entropy). |
So where does this leave us? If we take the laws of thermodynamics at face value then it would seem that all matter and space in the universe has always existed with a certain amount of energy.
And while this may be true on a grand scale it doesn’t explain how individual particles or small groups of particles came into existence with energy. It’s thought that our best current explanation for how particles come into existence with energy is through quantum fluctuations.
In quantum mechanics, there is a phenomenon known as zero-point energies whereby even supposedly “empty” space is not truly empty but instead contains tiny amounts of electromagnetic radiation and other types of energies. These fluctuations can cause virtual particles to spontaneously pop into and out of existence. While most of these virtual particles are quickly annihilated again they can sometimes interact long enough to become real particles.
It’s through these processes that new matter and energy come into existence in our universe despite the fact that overall the amount of matter and energy remains constant.
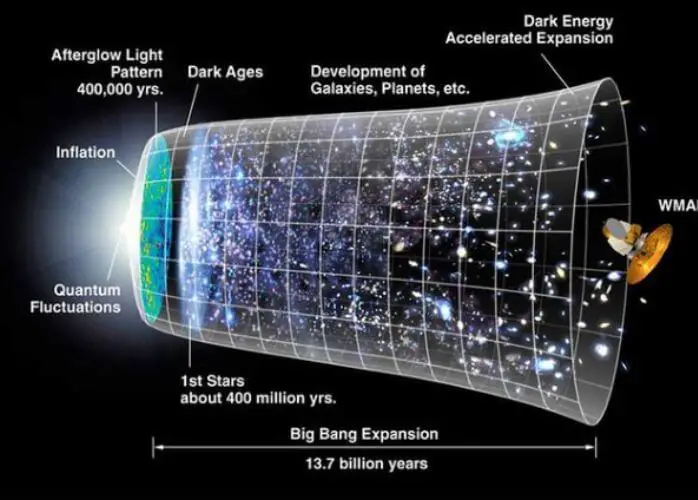
If Energy Cannot Be Created, How Did the Big Bang Happen?
In the beginning, there was nothing. No space, no time, no matter, no energy. Then, in a fraction of a second, it all changed.
The universe began with the Big Bang—the sudden appearance of space and time and an immense release of energy and matter. It was as if someone had lit a fuse on a powerful bomb. Today, we know that the Big Bang was not an explosion in the conventional sense; rather, it was the rapid expansion of space itself.
Energy and matter were created simultaneously as space expanded outward at faster-than-light speeds. The inflationary theory also tells us that during this brief period of inflationary expansion, quantum fluctuations in the energy field gave rise to tiny regions of slightly higher density than their surroundings. These regions eventually became galaxies, stars, and planets—the building blocks of our universe as we know it today.
So where did all this energy come from? According to current scientific understanding, it was borrowed from the future. In other words, it is possible to borrow energy from empty space itself—a phenomenon known as vacuum energy or zero-point energy.
This may sound like something out of science fiction, but it is actually a well-understood feature of quantum mechanics (the physics of very small things).
Why Is It Impossible to Consider All the Energy in the Universe When Doing Energy Calculations?
In order to calculate the energy in the universe, we would need to know the mass and volume of the universe. However, we don’t know either of those things for sure. The best estimates put the mass of the universe at around 10^53 kg and its diameter at around 10^26 m.
But these numbers come with a lot of uncertainty. And even if we knew them for sure, calculating the energy in the universe is an incredibly difficult task. The reason it’s so difficult is that there are so many different forms of energy in the universe.
There’s kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, light energy, dark energy, etc. And all of these forms of energy are constantly changing and interacting with each other. So trying to calculate the total amount of energy in the universe is like trying to hit a moving target.
But even if we could accurately calculate the amount of energy in the universe, it wouldn’t be very useful information. That’s because our understanding of physics tells us that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It can only be converted from one form to another.
So knowing the total amount of energy in existence doesn’t tell us anything about how that energy will be used or why certain events happen (like stars exploding). So while it might be interesting to know how much energy is contained within our vast and expanding cosmos, it’s an impossible task to accurately quantify it all.
Energy Cannot Be Created Or Destroyed Which Law?
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is constant, and never changing. The law is a fundamental principle of physics and has been proven through countless experiments over many years.
This law has important implications for our understanding of the universe. It means that energy can never be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another. For example, when a rock is dropped, the potential energy it had at the top of its arc is converted into kinetic energy as it falls.
Once it reaches the ground, all of its kinetic energy is converted into heat and sound energy. However, the total amount of Energy remains constant throughout this process; it is simply transformed from one form to another. Similarly, when we burn fossil fuels like coal and oil to generate electricity, we are not creating new energy; we are simply converting chemical Energy into electrical Energy.
And when we use that electricity to power our homes and office buildings, the Energy is again converted – this time into light and heat energy. Again, the total amount of Energy in the universe remains unchanged; we are just transforming it from one form to another.
Energy Cannot Be Created Or Destroyed True Or False
One of the most fundamental laws of physics is the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is always constant. So where does this leave us when it comes to renewable energy sources?
If energy cannot be created or destroyed, then it must come from somewhere else – and that’s exactly what happens with renewables. Solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into electrical energy, while wind turbines harness the power of the wind to generate electricity. Dirty solar panels can still generate electricity, but the amount of power they produce will be reduced. In both cases, we are taking advantage of natural resources that are constantly being replenished, making renewable energy a sustainable option for powering our homes and businesses.
Energy Cannot Be Created Nor Destroyed
The law of conservation of energy is one of the most important laws in physics. It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but only transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is always constant.
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental law of physics that has many applications in our everyday lives. For example, when you ride a bike, your legs push against the pedals to make the wheels turn. This transfer of energy from your legs to the wheels is possible because energy cannot be created or destroyed.
The same principle applies to all forms of energy, including electrical, chemical, and nuclear energy. The law of conservation of energy also has important implications for our understanding of the universe as a whole. If energy can neither be created nor destroyed, then it must have always existed and will continue to exist forever.
This means that the universe itself is eternal and will never come to an end!
Energy Cannot Be Created Or Destroyed Einstein
In his famous equation, E=mc2, Albert Einstein revealed that matter and energy are one and the same. This principle is known as the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed—it can only be transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is constant.
Although individual particles of matter or photons of light may be lost or gained, the sum total of all energy remains the same. The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle of physics and it has been verified by numerous experiments over the years. It’s also a cornerstone of our understanding of how the universe works.
So what does this all mean for us here on Earth? Well, it turns out that this principle has some pretty important implications for our everyday lives. For example, when we burn fossil fuels like coal and oil to generate electricity, we’re not really creating new energy—we’re just transforming it from one form (chemical potential energy) into another (electrical energy).
And when we use up that electrical energy, it doesn’t disappear into thin air—it gets converted into heat, which eventually dissipates into space.
If Matter Cannot Be Created Or Destroyed, Where Did It Come from?
In the physical sciences, the matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space. All matter is made up of atoms, which are the basic units of matter. The word “matter” comes from the Latin word mater, meaning “substance.”
Matter cannot be created or destroyed- only transformed. This means that the total amount of matter in the universe remains constant. However, we can see evidence that suggests that our universe is constantly expanding.
So where did all this matter come from? The answer lies in what scientists call the Big Bang Theory. This theory states that our universe began as a very small, very dense point called a singularity.
Suddenly, there was a huge explosion and all of the matter in our universe was created. As the universe continues to expand, more and more matter is being created- even though the total amount of matter stays constant. So there you have it!
The next time someone asks you where all this Matter came from, you can tell them it came from the Big Bang!
FAQs
How Can Universe Expand If It Infinite?
If the universe is infinite, then how can it expand? This is a question that has puzzled scientists and cosmologists for many years. The answer lies in the fact that the universe is not really expanding into anything.
Rather, space itself is expanding. Think of it this way: imagine you have a balloon with dots all over it. As you blow up the balloon, the distance between the dots gets bigger.
But the size of the balloon (and therefore the number of dots) stays the same. In a similar way, as space expands, the distance between galaxies gets bigger but galaxies themselves don’t change size. So what is causing space to expand?
We’re not sure exactly, but scientists think it has something to do with dark energy – a mysterious force that makes up most of our universe. As dark energy pushes outwards, it makes space expand faster and faster. And since there’s an infinite amount of dark energy in our universe, there’s no limit to how much space can continue to expand!
Where Did Energy Come from If It Cannot Be Created Or Destroyed?
In order to understand where energy comes from, we must first understand what energy is. Energy is the ability to do work. It is present in many forms, such as light, heat, electrical, chemical, nuclear, and gravitational potential energy.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed- it can only be transformed from one form to another. For example, when a candle burns, the wax is converted into heat and light energy. So, where did this energy come from originally?
The answer lies in the laws of thermodynamics- specifically the first law of thermodynamics. This law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed- only transformed. Therefore, the total amount of energy in the universe has always been constant.
It is important to note that while matter can be created or destroyed (as seen in nuclear reactions), energy can never be created or destroyed. So where did all this energy come from? According to scientists, it came from the Big Bang- the event that marked the beginning of our universe.
During this massive explosion, enormous amounts of energy were released and have been present ever since.
What Happens When the Universe Runs Out of Energy?
When the universe runs out of energy, it will no longer be able to sustain itself. The stars will go out, and all matter will eventually dissipate into nothingness. There is currently no scientific consensus on what exactly will happen when the universe reaches this point, but it is generally agreed that it will be an extremely long time from now.
How Can the Universe Be Expanded into Nothing?
In order to answer this question, we must first understand what the universe is. The universe is everything that exists; it is all of space and time and all matter and energy. It also includes all forces, such as gravity.
So, when we talk about the universe expanding, we are talking about everything in the universe moving away from each other. Now that we know what the universe is, we can address how it could be expanding into nothing. One theory is that the universe is expanding into a vacuum.
A vacuum is an area with no matter or energy in it. So, if the universe is expanding into a vacuum, then it would be expanding into nothing. Another theory about how the universe could be expanding into nothing has to do with dark energy.
Dark energy is a mysterious force that scientists believe makes up 68% of the universe. It seems to be pushing everything apart and causing the expansion of the universe to speed up over time. So, if dark energy continues to make the universe expand faster and faster, eventually everything will become so spread out that there will be nothing left except for empty space.
We don’t yet know for sure which of these theories (if either) is correct. But both show how it’s possible for the universe to keep expanding even though there’s nothing for it to expand into!
Conclusion
The blog post discusses the question of how the universe can be expanding if energy cannot be created. It explains that the answer lies in the fact that energy can be converted into matter, and vice versa. This conversion means that there is a constant supply of energy in the universe, even as it expands.