Batteries and battery management systems (BMS) are essential for electric vehicles (EVs) to function. Without a BMS, an EV would be unable to properly utilize its battery, leading to reduced range and performance. A BMS ensures that the battery is used optimally and safely.
It monitors the battery’s health, temperature, voltage, and current. The BMS then uses this information to determine how much power the battery can safely provide to the motor. If the BMS detects that the battery is getting too hot or too low on charge, it will take action to prevent damage.
This could involve reducing power output or shutting down the vehicle entirely.
The BMS, or battery management system, is a device used to protect lithium-ion batteries. When the BMS is connected to the battery, it will monitor the battery’s voltage and current. If the voltage or current gets too high, the BMS will shut off the power to prevent damage to the battery.
The BMS can also balance the cells in a lithium-ion battery pack so that they all have the same voltage. This prevents overcharging and extends the life of the battery.
How Are BMS Connected?
BMS are connected by what is called a bus. This bus allows all of the BMS to communicate with each other and share information. The most common type of bus is the CAN bus, which stands for Controller Area Network.
How Does BMS Work in a Battery?
How BMS Works in a Battery Batteries consist of cells that store energy. The cell is the basic unit of a battery, composed of many smaller units called electrodes.
- The electrodes are where the chemical reaction that produces electricity takes place. The BMS, or Battery Management System, is a device that monitors the voltage and current of each cell in a battery pack. It ensures that each cell is charged and discharged within its safe operating limits.
- It also balances the cells so that they all have the same voltage and prevents overcharging or deep discharging, damaging the cells. The BMS consists of a microcontroller, sensors, and MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors). The microcontroller constantly monitors the voltages of all the cells in the battery pack and controls the charging and discharging of each cell according to its needs.
- The sensors measure the temperature and current of each cell to prevent overheating or excessive discharge rates. And finally, MOSFETs are used to switch currents on and off very quickly; this allows for precise control over how much power flows into or out of each individual cell.
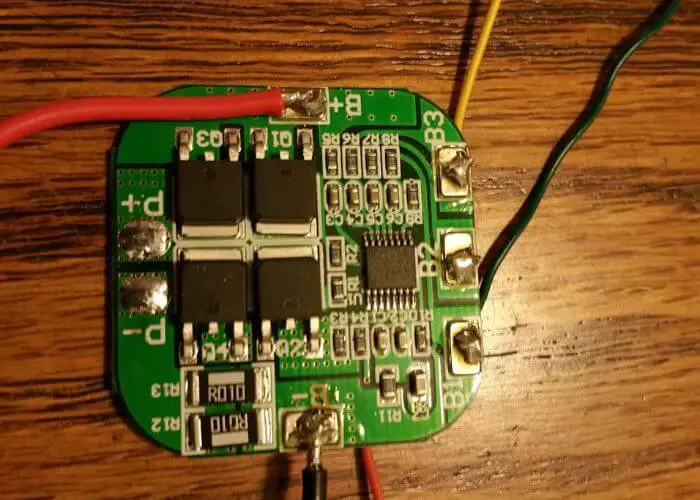
How Are BMS Wired?
BMS, or battery management systems, are a critical component in any lithium-ion battery pack. They provide several important functions, including:
| Number one | Monitoring the individual cell voltages to prevent overcharging or over-discharging. |
| Number two | Balancing the cells ensures even discharge and improves longevity. |
| Number three | Protecting short circuits, overheating, and other hazards. |
| Number four | Managing the charging and discharging of the battery pack. |
Most BMSs are wired in a parallel configuration, meaning that each cell in the battery is connected directly to the BMS. This allows the BMS to monitor each cell’s voltage individually and provides the best possible protection for the cells.
Some lower-cost BMSs may be wired in a series configuration, where each cell is connected to the next in the series rather than directly to the BMS.
This type of wiring can save on costs but sacrifices some safety and flexibility; it also makes balancing more difficult since cells can only be balanced relative to those immediately before and after them in series. regardless of how they’re wired internally, all BMSs have positive and negative terminals that must be connected to the corresponding terminals on the battery pack.
Make sure you connect these correctly – if you reverse them, the BMS will likely be damaged beyond repair!
Does a BMS Balance a Battery?
Batteries are made up of some cells connected in series. Each cell has a positive and negative electrode separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is being charged, electrons flow from the negative to the positive electrode, and when it is being discharged, they flow in the opposite direction.
A battery management system (BMS) is a device used to monitor and control the charging and discharging of a battery. It can protect the battery from overcharging or over-discharging and prevent damage from excessive heat or current. The BMS will balance the battery by equalizing the voltage across all of the cells in the battery.
This ensures that each cell is receiving the same amount of charge and prevents any one cell from becoming overloaded or undercharged. By keeping all of the cells in balance, the BMS prolongs the battery’s life and helps ensure its safety.
How to Connect BMS to Battery?
Are you looking to connect your Bms to a battery? If so, there are a few things you need to know before doing so.
Here is a quick guide on how to connect Bms to the battery:
Step One
Before connecting your BMS, make sure that the polarity of the connection is correct. Incorrect polarity can damage your BMS or cause it to malfunction.
Step Two
Once you have confirmed the correct polarity, use solder or wire nuts to make the connection.
It is also important to note that some BMS models have an internal fuse. If yours does, check the rating of the fuse and replace it if necessary.
Step Three
When making the connection, be sure to leave enough slack in the wires so that they can expand and contract as needed without putting strain on the connection points.
Final Step
Finally, once everything is connected, test your system before using it to ensure proper functioning.
How to Connect BMS in Series?
Batteries are a common power source for many devices and applications. Multiple batteries may sometimes be required to provide the necessary power. When multiple batteries are used, they must be connected in series or parallel to work together.
What is Series Connection?
A series connection is when batteries are connected end-to-end so that the voltage of each battery is added together. The current remains the same as it flows through each battery, but the total voltage will equal the sum of all the voltages of the individual batteries.
How to Connect BMS in Series?
Follow the step-by-step guideline to connect BMS In series:
| Step one | First, identify how many volts (V) your application requires and how many amp hours (Ah) you need. This will determine how many batteries you’ll need and what size they should be. For example, the 100 amp BMS refers to the maximum current that the system can handle. |
| Step two | Once you have your batteries, connect them end-to-end using jumper cables or other means so that their positive (+) and negative (-) terminals are touching. Make sure that there is no break in the circuit between any of the batteries! |
| Step three | That’s it! Your application should now have access to the increased voltage provided by all of the connected batteries. Remember that if one battery fails, then all power will be lost, so it’s essential to use high-quality batteries and keep spares on hand, just in case. |
How to Select BMS for Battery Pack?
Batteries are a critical component in any electrical system. Without them, our devices would be useless. So when it comes to choosing the right battery management system (BMS) for your needs, it’s essential to know what factors to consider. We have a detailed article on this topic; click here to read it.
Here are four key things to keep in mind when selecting a BMS for your next project:
| Voltage and current requirements | You first need to consider your device’s or system’s voltage and current requirements. What is the maximum voltage and current that your system can tolerate? Make sure the BMS you select can handle these ratings. |
| Capacity | Another important consideration is the capacity of the BMS. How many batteries does it need to manage? What is the total capacity of all the batteries in your system? Make sure the BMS can handle the number of batteries and their total capacity. |
| Charge/Discharge Rate | You also need to consider how fast you need to charge or discharge your batteries. What is the maximum charge/discharge rate of your system? Make sure the BMS can handle this rate without compromising safety or performance. |
What is BMS Wiring?
BMS Wiring is a system of electrical circuits and components that distributes power to devices and appliances in a home or office.
- The main purpose of BMS Wiring is to provide a safe and efficient means of delivering electricity to all the areas where it is needed. Many different types of Bms Wiring systems are available, but they all share some basic features.
- All BMS Wiring systems have three main parts: the service panel, the distribution panel, and the wiring itself. The service panel is the central point from which power flows into the home or office. It contains circuit breakers or fuses that protect the home’s electrical system from overloads.
- The distribution panel then sends power to individual circuits throughout the building. Finally, the wiring runs back to the distribution panel from outlets and fixtures. BMS Wiring systems can be either AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current).
- AC systems are more common in homes, while DC systems are typically used in industrial settings. AC systems use a voltage alternating between positive and negative values, while DC voltage always flows in one direction. Both types of systems can pose serious dangers if not installed correctly.
What is BMS in Battery?
Batteries are devices that store electrical energy and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. A battery comprises one or more cells, each containing a positive electrode (the anode) and a negative electrode (the cathode), separated by an electrolyte. When the cell is connected to an external circuit, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, producing DC electricity.
The term “battery” refers to a device consisting of two or more cells connected together in series or parallel. The terms “primary battery” and “secondary battery” refer to batteries that cannot be recharged after use (primary batteries) and those that can be recharged (secondary batteries). Batteries are used in many applications, including automotive starter batteries, backup power for computers and other electronic equipment, portable electronics such as laptop computers and cellular phones, and electric vehicles.
The word “BMS” stands for Battery Management System. A BMS is a system that monitors and manages the charging and discharging of a battery pack. It is typically used in conjunction with rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
The BMS ensures that each cell in the battery pack is charged and discharged evenly, thus prolonging the life of the battery pack. In some cases, the BMS will also provide over-charge protection, over-discharge protection, short-circuit protection, and thermal runaway protection.
Wrap Up
Used Resources: