Batteries store energy in the form of chemical reactions. The battery contains two electrodes, a positive and a negative, that are separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is hooked up to a circuit, the electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the electrolyte.
This flow of electrons produces an electric current that can be used to power electrical devices.
Batteries store energy, but they don’t store power. Power is the rate at which energy is used up, and it’s determined by the load on the battery. The higher the load, the faster the battery will discharge.
Do Batteries Store Energy As Chemical Energy?
Batteries are devices that store energy in the form of electrical potential energy. This potential energy is converted into chemical energy, which is then used to power electronic devices. The chemical reaction that occurs within the battery creates an electric current that can be used to power electronic devices.
The most common type of battery is the lead-acid battery, which uses a chemical reaction between lead and sulfuric acid to create electrical current. Lead-acid batteries are typically found in automobiles and other vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries are another common type of battery, and these use a chemical reaction between lithium and oxygen to create electrical current.
Lithium-ion batteries are often found in laptop computers and cell phones.
What is the Form of Energy That Batteries Store Energy?
Batteries store energy in the form of chemical potential energy. This type of energy is stored in the bonds between atoms and molecules. When a battery is connected to an electrical circuit, the chemical potential energy is converted into electrical energy.
Why Do Batteries Run Out of Power?

Batteries are a common power source for many devices, from flashlights to cell phones. But why do batteries run out of power? The answer has to do with the chemical reaction that takes place inside the battery.
This reaction is what produces the electrical current that powers your device. Over time, however, the chemicals in the battery start to run out. When this happens, the battery can no longer produce enough electrical current to power your device.
And that’s why batteries eventually die. There are ways to prolong the life of your battery, however. For example, you can avoid leaving your device plugged in for long periods of time, as this can drain the battery more quickly.
You can also try not to use your device in extreme temperatures, as this can also affect battery life. By following these simple tips, you can help ensure that your battery lasts as long as possible.
Do Batteries Store Electricity?
Batteries are devices that store electricity. A battery has one or more cells, each of which contains a chemical reaction that produces electrons. The battery uses these electrons to generate an electric current when it is connected to a circuit.
Batteries come in many shapes and sizes, from small button batteries used in watches to large lead-acid batteries used in cars. The type of battery you need depends on the device you want to power and the amount of time you need the device to operate.
Button batteries are typically made of lithium or mercury, while lead-acid batteries are made of lead and acid.
Lead-acid batteries are usually much larger than button batteries and can provide a higher current for longer periods of time.
How Do Batteries Produce Electricity?
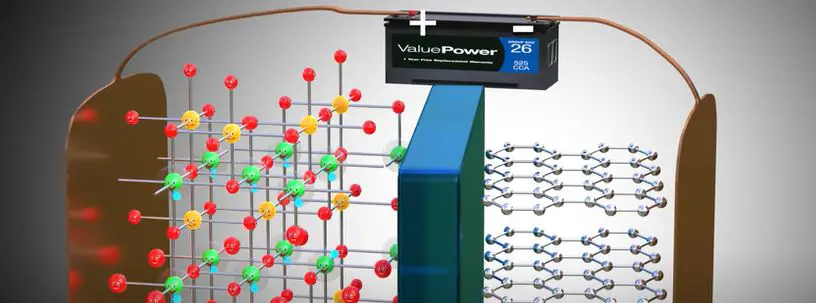
Batteries are a common source of electricity, but how do they work? Batteries produce electricity through a chemical reaction between two electrodes and an electrolyte. The electrodes are made of different materials, one of which is typically metal.
The electrolyte is usually an acidic solution. When the two electrodes are connected by a conducting material, such as a wire, the reaction between them creates an electric current.
The strength of the current produced by a battery depends on the materials used for the electrodes and electrolyte, as well as the size of the battery.
Smaller batteries tend to produce weaker currents than larger ones.
What Does a Battery Do in a Circuit?
A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and converts it to electrical energy. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Each cell has two electrodes, a positive electrode (the anode) and a negative electrode (the cathode), separated by an electrolyte.
When the battery is connected to an external circuit, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the electrolyte and the external circuit. This flow of electrons produces direct current (DC). The function of a battery in a circuit is to provide power to that circuit.
Without a battery, most circuits would not be able to function because they would not have enough power to operate. The battery provides this power by converting its stored chemical energy into electrical energy which can then be used by the components in the circuit.
How Does a Battery Work?
A battery is a device that stores energy and converts it into electricity. The basic principle behind how a battery works is converting chemical energy into electrical energy. This conversion process happens through a series of reactions between the positive and negative electrodes, also known as the anode and cathode, respectively, and the electrolyte.
The Positive Electrode or Anode
The positive electrode or anode, is where oxidation occurs. During this process, electrons are released from the atoms in the anode material and flow through the external circuit to the negative electrode, or cathode. At the same time, ions flow from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte.
The Negative Electrode or Cathode
The negative electrode, or cathode, is where reduction occurs. In this process, electrons are received by atoms in the cathode material and combine with ions flowing from the anode. This combination results in water molecules being formed as a product of the reaction.
The Chemical Reactions
The chemical reactions that occur inside a battery generate electrical energy that can be used to power devices such as cell phones, flashlights, and computers. Batteries come in many different sizes and shapes to accommodate different needs.
How are Batteries Made?
Batteries are made up of three major parts: the anode, the cathode, and the electrolyte. The anode is made of carbon, while the cathode is usually made of lithium. The electrolyte is what allows electrons to flow between the two electrodes, and it is typically made of a saltwater solution.
To make a battery, manufacturers first create the anode and cathode using foil sheets. They then cut these sheets into thin strips and roll them into cylinders. Next, they stack the rolled sheets together and weld them at their edges.
This creates a “jellyroll” which is then placed into a plastic case that serves as the battery’s housing.
The final step is to fill the jellyroll with electrolyte and seal it off. Once this is done, the battery is ready to be used!

Do Batteries Store Energy?
Batteries are devices that store energy and release it when needed. The most common type of battery is the lead-acid battery, which is used in cars and trucks. Lead-acid batteries work by converting chemical energy into electrical energy.
The chemical reaction inside the battery creates electrons, which flow through the wires to create an electric current. When the battery is not being used, the electrons are stored in the lead plates. When the battery is being used, the electrons flow from one plate to another, creating an electric current.
What Type of Energy is Stored in a Battery?
A battery is a device that stores energy in the form of electric potential energy. The word “battery” comes from the Italian batteria, which means “a group of things.” A battery consists of one or more cells, each of which contains a chemical reaction that can produce an electric current.
When the cell is connected to an external circuit, the chemical reaction produces an electric current that flows through the circuit and does work on any devices connected to it.
Batteries come in many different sizes and shapes, but all have three basic parts: an anode (the negative electrode), a cathode (the positive electrode), and an electrolyte (a substance that conducts electricity). The electrolyte is usually a solution of sulfuric acid or another acidic compound.
When the cell is connected to an external circuit, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the electrolyte and the external circuit. This flow of electrons produces an electric current.
Conclusion
Batteries store energy, which is measured in watt-hours (Wh). The capacity of a battery is the amount of energy it can store, usually expressed in amp-hours (Ah). A battery’s power is the rate at which it can deliver that energy, usually expressed in watts (W).