The sun is the Earth’s primary source of energy. Solar radiation provides the energy that drives the Earth’s climate and weather. It also supports the growth of plants and other organisms.
About 30 percent of the sunlight that hits the Earth is reflected back into space. The rest is absorbed by the atmosphere, oceans, land surfaces, and clouds.

The sun is the Earth’s primary source of energy, providing more than enough to power all of the planet’s needs. But what percentage of the sun’s energy actually makes it into the Earth’s system? It turns out that a surprisingly small amount of sunlight is actually absorbed by the Earth.
Just 26% of incoming solar radiation is absorbed by land and oceans, while the rest is reflected back into space. Cloud cover also has a significant impact on how much sunlight reaches the surface, with an estimated 20-25% of sunlight being reflected back into space by clouds. So why isn’t more sunlight absorbed? The answer lies in the Earth’s atmosphere, which acts as a natural filter.
Gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor absorb some of incoming sunlight, preventing it from reaching the surface. This helps to regulate the planet’s temperature, keeping it habitable for life. While just a fraction of sunlight is needed to power our planet, we must be careful not to overload our atmosphere with greenhouse gases that can trap too much heat and lead to global warming.
By working together to reduce emissions, we can help keep our planet healthy and sustainable for future generations.
How Much of the Sun’s Energy is Absorbed into the Earth’s System?
The sun is the Earth’s largest source of external energy. Solar radiation, or sunlight, warms our planet and drives the Earth’s climate and weather. About 30 percent of the sun’s energy is reflected back into space by clouds, particles in the atmosphere, and surfaces like snow and ice.
The rest is absorbed by land, air, oceans, and life on Earth. Of the solar energy that reaches the ground, about half is immediately returned to space as infrared radiation (heat). The amount of heat retained by the Earth varies depending on a number of factors including cloud cover, atmospheric composition (greenhouse gases), surface reflectivity (albedo), and latitude.
Depending on these conditions, between 51-79% of incoming sunlight is absorbed at the surface layer of the Earth. Once absorbed, this heat is redistributed around the globe by ocean currents and winds.
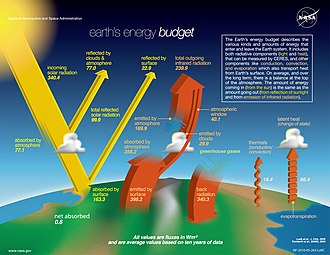
What is the Total Percentage of Solar Energy Absorbed?
Solar energy is the energy that comes from the sun. It is the most abundant form of renewable energy and can be used in many different ways. The total percentage of solar energy absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and land masses is approximately 3,850,000 EJ per year.
Of this amount, about 30% is reflected back into space while the rest is absorbed by the atmosphere, oceans, and land masses. The total solar radiation absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, and landmasses daily is approximately 42 EJ.
What Type of Energy Does the Earth Emit into the Atmosphere?
The earth emits a variety of energy into the atmosphere, including visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared radiation, and x-rays. Each type of energy has different effects on the atmosphere.
Visible Light
Visible light is the most familiar form of energy emitted by the earth. This type of light makes up the colors of the rainbow and is responsible for day and night.
Ultraviolet Light
Ultraviolet light is invisible to human eyes but can be seen using special instruments. This type of radiation is harmful to living things and can cause skin cancer.
Infrared Radiation
Infrared radiation is also invisible to human eyes but can be felt as heat. This type of radiation helps keep us warm in cold weather.
X-rays
X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate solid objects. X-rays are used in medical imaging and security screening.
The energy emitted by the earth affects the atmospheric composition, climate, and weather patterns. The sun’s ultraviolet rays help break down ozone molecules in the stratosphere, which protects us from harmful UV rays reaching the ground.
How Much Energy is Reflected by the Atmosphere Absorbed?

The sun is the ultimate source of energy for our planet. Its energy is radiated outwards in the form of electromagnetic waves, which travel through space until they reach Earth. Once here, some of the sun’s energy is reflected back into space by clouds and particles in the atmosphere, while the rest is absorbed by the land and oceans.
How much of the sun’s energy is reflected back into space? It turns out that this number varies depending on a number of factors, including cloud cover, atmospheric composition, and the angle at which sunlight hits Earth’s surface. For example, when sunlight strikes a sandy beach at a low angle, more light is reflected than when it strikes at a high angle.
In general, however, it is thought that about 30% of sunlight that reaches Earth’s atmosphere is eventually reflected back into space. This means that 70% of the sun’s energy is absorbed by our planet. Of this amount, 19% goes towards evaporating water from lakes and oceans (a process known as evapotranspiration), while 51% warms up the land surface.
The remaining 50% of solar radiation penetrates through to the earth’s interior where it warms up rocks and soil.
How Much Solar Energy Reaches the Earth’S Surface?
How Much Solar Energy Reaches the Earth’S Surface? The sun is the ultimate source of all energy on earth. All life forms depend on solar radiation to maintain their body temperatures and to grow.
The amount of solar radiation that reaches the earth’s surface varies depending on location, time of year, and weather conditions. In general, however, about 1,000 watts of sunlight per square meter strikes the planet’s atmosphere each day. This means that in one hour, more than enough sunlight falls on earth to provide each person with almost four years’ worth of their daily energy needs!
While most of us are not able to harness this power directly, we can capture some of it using solar panels. Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic cells (PV cells) that convert sunlight into electricity. When photons from the sun hit a PV cell, they knock electrons loose from atoms. Before using solar panel select the best side of your house.
These free-flowing electrons can be harnessed as an electrical current. By hooking PV cells up in series, we can create larger voltages and generate enough electricity to power our homes and businesses. Solar panels are becoming increasingly popular as people look for ways to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and lower their carbon footprints.
However, there are still some challenges associated with solar power technology. For example, PV cells only convert about 20% of the incoming sunlight into electricity; the rest is lost as heat. Additionally, solar panel arrays can be quite expensive to install initially.
But with continued research and development, it is likely that these drawbacks will eventually be overcome. And in the meantime, we can all do our part by making use of solar-powered products whenever possible!
Solar Radiation And Earth’S Energy Balance
The sun is the ultimate source of all energy on Earth. Solar radiation–the sun’s electromagnetic radiation–provides the energy that drives our planet’s climate and weather. It also fuels the growth of plants, which in turn provide food and shelter for animals, and ultimately support human life.
Solar radiation is a type of energy that travels through the vacuum of space. The sun emits a broad spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, but only a small portion of this radiation reaches Earth. The amount of solar radiation that reaches our planet’s atmosphere depends on two things: the distance between the sun and Earth, and atmospheric conditions (such as cloud cover).
Earth’s orbit around the sun is not perfectly circular, so our distance from the sun varies throughout the year. This variation has a small effect on the amount of solar radiation that reaches us; however, it is much less important than atmospheric conditions. For example, when there are more clouds in the sky, less solar radiation reaches Earth’s surface because some of it is reflected back into space before it ever has a chance to reach us.
Additionally, when air pollution particles are present in the atmosphere they can scatter or absorb sunlight before it reaches Earth’s surface, further reducing the amount of solar radiation that we receive. The balance between incoming and outgoing energy determines Earth’s average global temperature. When there is more incoming energy than outgoing energy (due to factors like an increase in greenhouse gases), average global temperatures will rise; when there is more outgoing energy than incoming energy (such as during volcanic eruptions), average global temperatures will decrease.
Our planet’s climate has changed many times over its 4.5-billion-year history due to variations in these factors; however, since industrialization began around 150 years ago human activity has become increasingly responsible for changing Earth’s climate by altering the balance between incoming and outgoing radiant energy.
Earth Energy Balance Equation
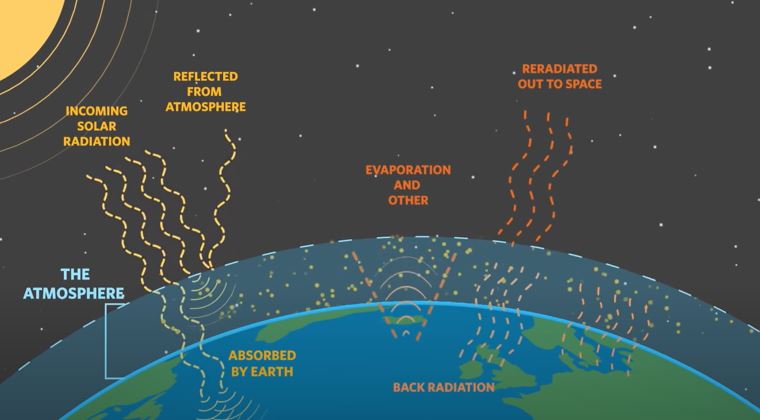
Earth’s energy balance equation is the difference between the amount of solar radiation absorbed by the planet and the infrared radiation emitted back into space. This equation is important in understanding how Earth’s climate works and how it can be affected by human activities.
The main component of Earth’s energy balance equation is the sun.
The sun emits a large amount of radiation, some of which is visible light that we see every day. But the sun also emits invisible infrared radiation, which makes up a large portion of its total output. When this infrared radiation reaches Earth, some of it is absorbed by greenhouse gases in our atmosphere, causing our planet to warm.
The rest of the sunlight is reflected back into space by clouds and other particles in the atmosphere.
Earth also emits infrared radiation back into space, but at a much cooler temperature than the sun. This happens because Earth has warmed due to all of the incoming solar radiation that it absorbs.
Some of this outgoing infrared radiation escapes directly into space, but some of it gets trapped in our atmosphere by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor. This process keeps our planet warm enough for life to exist!
Human activity can affect Earth’s energy balance equation by changing the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere.
For example, burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the air, which can trap more heat and cause Earth to warm even further. That’s why it’s so important to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and find cleaner sources of energy!
About 30 Percent of Incoming Solar Energy is
Reflected Back Into Space
The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for our planet. The sun’s energy drives the water cycle, powers the winds, and provides warmth and light that allow plants to grow.
This solar energy also fuels the Earth’s climate. About 30 percent of the sunlight that strikes Earth is reflected back into space. The atmosphere and clouds reflect some sunlight back into space, as do snow-covered surfaces, deserts, and bodies of water.
When this reflected sunlight reaches Earth’s surface again, it has less energy than direct sunlight because it has been scattered and absorbed by atmospheric gases and particles. This “re-radiated” sunlight still contributes to warming Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
Conclusion
The sun is the Earth’s primary source of energy and drives the planet’s climate and weather. About 30 percent of the sunlight that hits the Earth is reflected back into space. The rest is absorbed by the atmosphere, land, and oceans.
Of that absorbed sunlight, about 19 percent goes into heating the atmosphere, while the remainder warms the surface of the planet.